

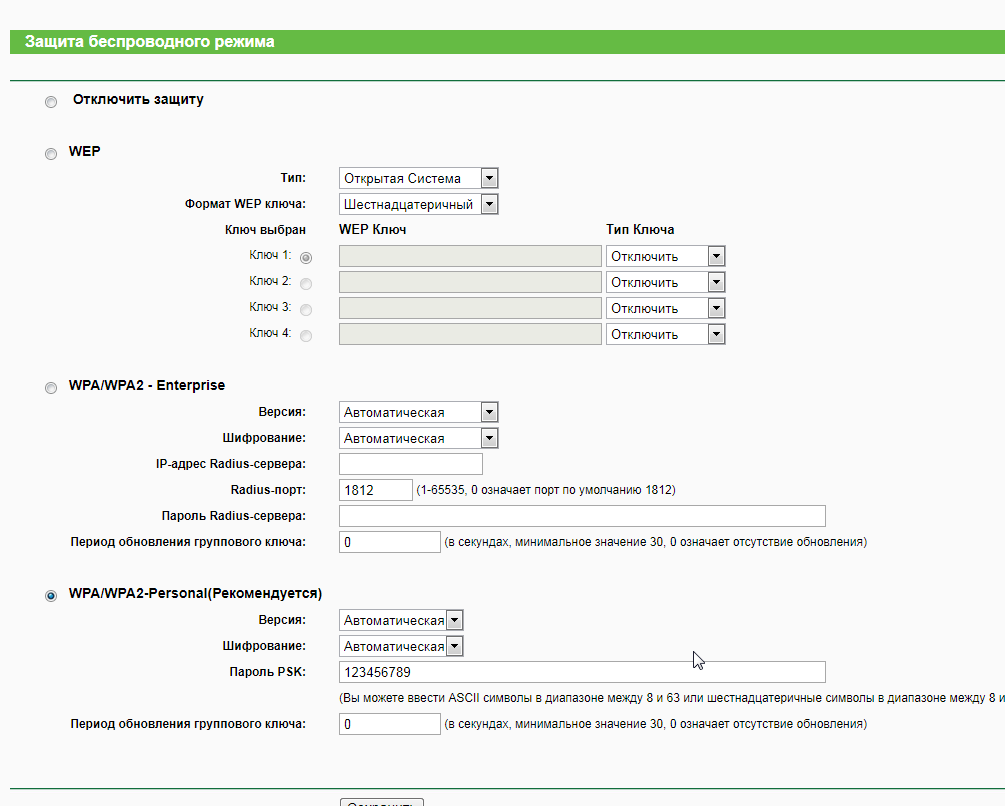
If you use encryption, all wireless devices on your wireless network must use the same encryption keys. For stronger security, you should use a 128-bit key. WEP encryption provides for two levels of security, using a 64-bit key (sometimes referred to as 40-bit) or a 128-bit key (also known as 104-bit). Only computers that use the same encryption key can access the network and decrypt the data transmitted by other computers. WEP uses an encryption key to encrypt data before transmitting it. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) uses encryption to help prevent unauthorized reception of wireless data. The client access is granted only if it passes a challenge-based authentication. Shared key authentication requires that the client configure a static WEP key. You can share this secret key via a wired Ethernet connection, or by physically using a USB memory stick or CD. When shared key authentication is used, each wireless station is assumed to have received a secret shared key over a secure channel that is independent from the 802.11 wireless network communications channel.If no encryption is enabled on the network, any device that knows the Service Set Identifier (SSID) of the access point can gain access to the network. Open authentication allows any device to gain network access. The receiving station or access point grants any request for authentication. The station that needs to authenticate with another wireless station sends an authentication management request that contains the identity of the sending station. When open authentication is used, any wireless station can request authentication.IEEE 802.11 supports two types of network authentication methods: Open System and Shared Key. Personal Security Methods Open and Shared Network Authentication (This is not set at the adapter using the Intel® PROSet/Wireless WiFi Connection Utility, it is set at the access point.) Only those computers with knowledge of the SSID can access the network. SSID BroadcastingĪ simple way to improve network security is to set your network access point to not broadcast the Service Set Identifier (SSID). Encryption keys are available with two levels of security, 64-bit and 128-bit. Only computers equipped with pre-shared keys can encrypt and decrypt the data being transmitted. You can select encryption algorithms to encrypt the information and data that is sent across your wireless network. Once authentication is completed and access is granted, the client has access to the network.
AuthenticationĪuthentication is the process of identifying and approving a request from a client (usually a laptop) to access a network at a network access point. You can easily protect your home and small business network from nearly all forms of unauthorized access with the security methods described in this section. Your wireless network, if left unprotected, is vulnerable to access from other computers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
